The Data Handbook
How to use data to improve your customer journey and get better business outcomes in digital sales. Interviews, use cases, and deep-dives.
Get the bookDon’t settle for what’s available
What makes Shopify a great eCommerce platform is its customisability. Shopify gives you full control about the look and feel of your shop, and Shopify apps play a big role in this. Every year, developers publish hundreds of new apps to the Shopify App Store to solve all kinds of problems merchants might face.
But what if none of the existing apps fit your needs? Well, developing a Shopify app is actually not at all difficult. Shopify has very extensive documentation on how to get started with building your own app and how to use their many APIs.
Furthermore, Shopify is language agnostic, meaning that it's up to you what programming language you want to use. This is due to the fact that your Shopify app must be self-hosted and all interactions with Shopify happen through Shopify's well defined REST APIs using JSON.
In addition, you can decide whether you want to create a public or a private Shopify app. Whilst public apps can be installed by any store, private apps are tailored to your needs and will only work in your own store.
Go JavaScript all the way – or don’t
To make things easier for you, Shopify provides official libraries for Ruby and Python, but third-party libraries are also available for other languages such as Node or PHP. If you plan on providing a user interface for your app in the Shopify admin, and you most likely should, Shopify Polaris is your friend.

Polaris is Shopify's design system that helps you to create a user interface that is consistent with Shopify's native UI. Apart from guidelines on visuals and content, the most exciting part of Polaris is that it includes a React component library. The components provided by Polaris are easy to use, well documented, and fit right into Shopify's UI. As a result, no HTML or CSS skills are needed, just plain old JavaScript. Polaris allows you to be very productive by leveraging powerful JavaScript libraries like React and Redux. Even if you don't want to use React, Polaris also provides HTML snippets for all its React components.
Prepare for some very minor hair-pulling
Nonetheless, developing Shopify apps also has its downsides. The first commit to Polaris' GitHub repo was made in April 2017 and it shows. Whilst the React components provided by Polaris look polished and are easy to use, they are also somewhat limited. If you want to use a component differently from how it was intended to be used, you're out of luck and have to get creative to find workarounds.
Since Polaris is built on React, you can always create your own components and apply your own, custom, CSS. However, relying on CSS hacks isn't quite the definition of a clean code base and future Polaris releases might easily break your CSS.
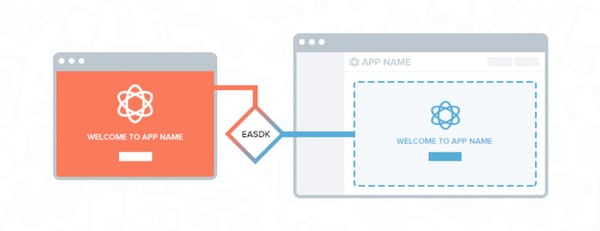
In addition, testing your app during development isn't as straightforward as you might expect, especially if you are building an embedded app. Embedded apps are Shopify apps that run directly in the Shopify admin and are loaded in an iFrame, as shown above. This allows embedded apps to utilise Shopify's Embedded App SDK to communicate with Shopify directly. The issue here is that Shopify uses HTTPS for all its websites, meaning you can't simply connect to your localhost during development due to mixed content restrictions. A possible workaround for this is to connect to your localhost using an SSL tunnel. A popular tool for this is ngrok.
In the end, despite its rather small downsides, Shopify provides powerful yet developer friendly tools to extend your store's functionality to your liking.
This is how I did it: my toy app Journey
As a small example, here’s a showcase of a toy app that I built in order to familiarise myself with Shopify app development. It’s a sales app called Journey and the general idea behind is to help customers find the right product for their needs.
Some products, like snowboards or bikes, come in many variations and it’s not easy for new customers to figure out which variant is the best for them. This is where Journey comes into play. It allows store owners to abstract complicated questions to simpler questions that every customer should be able to answer. For example, when buying a snowboard, the question of finding the right shape for a customer’s needs could be simplified to “What do you want to do with your snowboard?” and the answer is then mapped to some snowboard shape.
In the screenshot below you can see the embedded admin interface that is built with React and Shopify’s Polaris components. In this interface the store owner can choose a set of products, define questions and possible answers as well as their mapping. All questions are combined into a questionnaire and sent to the backend to save it.
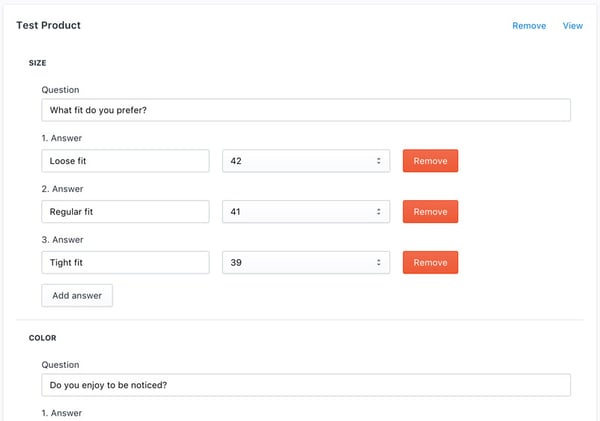
The backend, apart from storing questionnaires, serves as an application proxy to integrate the questionnaire into a customer’s store. What’s neat here is that by setting the content type of our response to “application/liquid”, we can dynamically adapt the style of our HTML to the theme of the store.
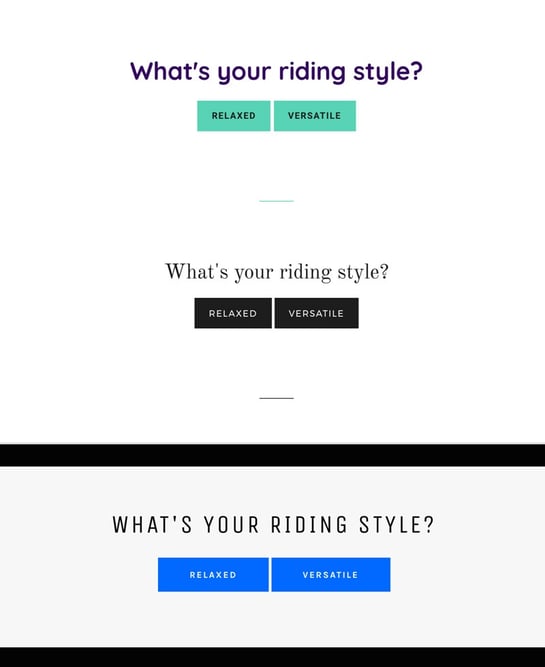
In the screenshot above you can see the front end rendering of the first question of a possible questionnaire. Admittedly, the generated HTML is rather simple and it comes with only minimal CSS, but it’s just a toy app after all.
The Journey app was originally inspired by the shopping experience on BikeID's website. If you're interested in learning more about how to create a purchase funnel that actually converts, I recommend you take a look at my colleague Victoria's post on that.
P.S. We're looking for nice people with a 'get shit done' attitude to join our team at Columbia Road! Take a new leap in your career, we have open positions in all business areas. Send a message, call us, visit us — we'd be thrilled to hear from you!
The Data Handbook
How to use data to improve your customer journey and get better business outcomes in digital sales. Interviews, use cases, and deep-dives.
Get the book




